
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug Regimen
- The Efficacy and Safety of Moderate-Intensity Rosuvastatin with Ezetimibe versus High-Intensity Rosuvastatin in High Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized, Multicenter, Open, Parallel, Phase 4 Study
- Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Sang Soo Kim, Hye Soon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Ji Hyun Lee, Inkyu Lee, Bo Kyeong Lee, Kyu Chang Won
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):818-825. Published online November 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0171
- 2,367 View
- 242 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
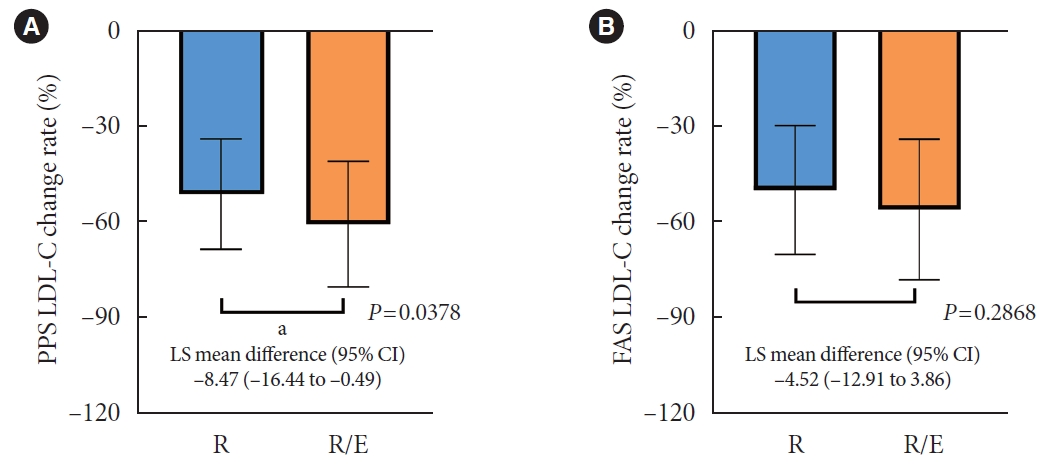
To investigate the efficacy and safety of moderate-intensity rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination compared to highintensity rosuvastatin in high atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This study was a randomized, multicenter, open, parallel phase 4 study, and enrolled T2DM subjects with an estimated 10-year ASCVD risk ≥7.5%. The primary endpoint was the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) change rate after 24-week rosuvastatin 10 mg/ezetimibe 10 mg treatment was non-inferior to that of rosuvastatin 20 mg. The achievement proportion of 10-year ASCVD risk <7.5% or comprehensive lipid target (LDL-C <70 mg/dL, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL, and apolipoprotein B <80 mg/dL) without discontinuation, and several metabolic parameters were explored as secondary endpoints.
Results
A hundred and six participants were assigned to each group. Both groups showed significant reduction in % change of LDL-C from baseline at week 24 (–63.90±6.89 vs. –55.44±6.85, combination vs. monotherapy, p=0.0378; respectively), but the combination treatment was superior to high-intensity monotherapy in LDL-C change (%) from baseline (least square [LS] mean difference, –8.47; 95% confidence interval, –16.44 to –0.49; p=0.0378). The combination treatment showed a higher proportion of achieved comprehensive lipid targets rather than monotherapy (85.36% vs. 62.22% in monotherapy, p=0.015). The ezetimibe combination significantly improved homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function even without A1c changes (LS mean difference, 17.13; p=0.0185).
Conclusion
In high ASCVD risk patients with T2DM, the combination of moderate-intensity rosuvastatin and ezetimibe was not only non-inferior but also superior to improving dyslipidemia with additional benefits compared to high-intensity rosuvastatin monotherapy.
- Basic Research
-
- The Effects of Exercise and Restriction of Sugar-Sweetened Beverages on Muscle Function and Autophagy Regulation in High-Fat High-Sucrose-Fed Obesity Mice
- Didi Zhang, Ji Hyun Lee, Hyung Eun Shin, Seong Eun Kwak, Jun Hyun Bae, Liang Tang, Wook Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):773-786. Published online March 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0157
- 7,080 View
- 252 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
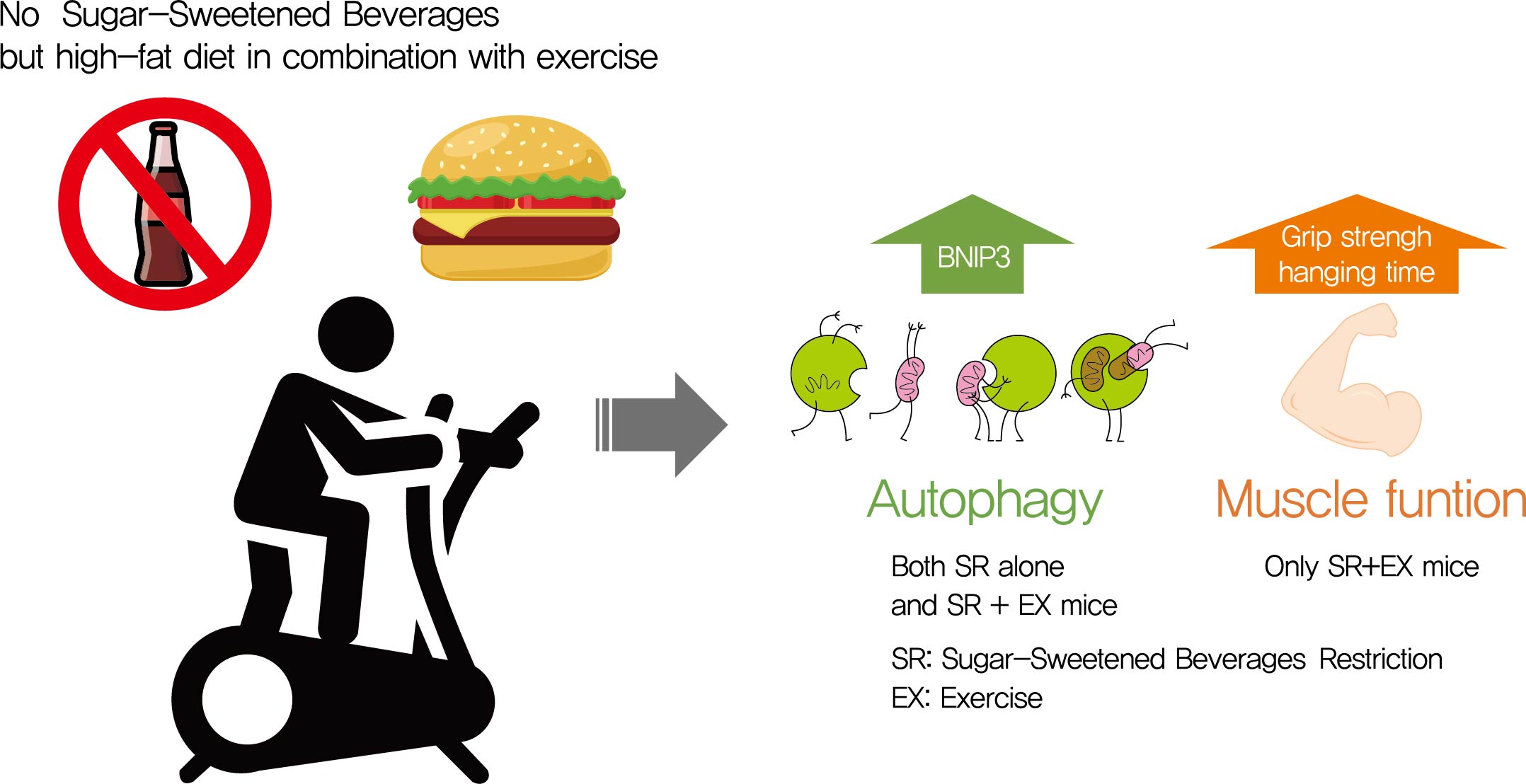
Autophagy maintains muscle mass and healthy skeletal muscles. Several recent studies have associated sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) consumption with diseases. We investigated whether muscle dysfunction due to obesity could be restored by SSB restriction (SR) alone or in combination with exercise (EX) training.
Methods
Obese mice were subjected to SR combined with treadmill EX. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test, grip strength test, hanging time test, and body composition analysis were performed. Triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) serum concentrations and TG concentrations in quadriceps muscles were analyzed. Western blot and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction helped analyze autophagy-related protein and mRNA expression, respectively.
Results
SR alone had no significant effect on fasting blood glucose levels, glucose tolerance, and muscle function. However, it had effect on serum TC, serum TG, and BCL2 interacting protein 3 expression. SR+EX improved glucose tolerance and muscle function and increased serum TC utilization than SR alone. SR+EX reduced P62 levels, increased glucose transporter type 4 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α protein expression, and improved grip strength relative to the high-fat and high-sucrose liquid (HFHS) group, and this was not observed in the HFHS+EX group.
Conclusion
SR induced mitophagy-related protein expression in quadriceps, without affecting muscle function. And, the combination of SR and EX activated mitophagy-related proteins and improved muscle function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inter-Organ Miscommunications in T2D Progression
Rajakrishnan Veluthakal, Diana Esparza, Joseph M. Hoolachan, Rekha Balakrishnan, Miwon Ahn, Eunjin Oh, Chathurani S. Jayasena, Debbie C. Thurmond
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(3): 1504. CrossRef - The association between healthy beverage index and sarcopenia in Iranian older adults: a case-control study
Marzieh Mahmoodi, Zainab Shateri, Mehran Nouri, Mohebat Vali, Nasrin Nasimi, Zahra Sohrabi, Mohammad Hossein Dabbaghmanesh, Maede Makhtoomi
BMC Geriatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Association between sugar-sweetened beverage consumption frequency and muscle strength: results from a sample of Chinese adolescents
Yunjie Zhang, Pan Xu, Yongjing Song, Nan Ma, Jinkui Lu
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle strength and prediabetes progression and regression in middle‐aged and older adults: a prospective cohort study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Duolao Wang, Tongzhi Wu
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(2): 909. CrossRef - INTENSITY OF FREE RADICAL PROCESSES IN RAT SKELETAL MUSCLES UNDER THE CONDITIONS OF DIFFERENT DIETARY SUPPLY WITH NUTRIENTS
O.M. Voloshchuk, Н.P. Kopylchuk
Fiziolohichnyĭ zhurnal.2022; 68(4): 48. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inter-Organ Miscommunications in T2D Progression
- Response: Adipokines and Insulin Resistance According to Characteristics of Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (
Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:457-65) - Eon Ju Jeon, Ji Hyun Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(1):90-91. Published online February 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.1.90
- 3,164 View
- 31 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of miR-152-Mediated Targeting of SOCS3 on Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Mice
Yuanchun Li, Li Kang, Juanjuan Huang, Juan Zhang, Chunhua Liu, Wenjuan Shen
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 361(3): 365. CrossRef
- Effects of miR-152-Mediated Targeting of SOCS3 on Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Adipokines and Insulin Resistance According to Characteristics of Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Eon Ju Jeon, Seong Yeon Hong, Ji Hyun Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):457-465. Published online November 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.457
- 3,900 View
- 40 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to evaluate adipokines concentration and insulin resistance according to maternal age or obesity at pregnancy and weight change at diagnosed gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in pregnant women with GDM.
Methods This study included 57 pregnant women who were diagnosed with GDM at 24 to 28 weeks of gestation. The subjects were classified into two or three groups according to pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI, <25 kg/m2 vs. ≥25 kg/m2), maternal age at pregnancy (<35 years old vs. ≥35 years old), and weight change during pregnancy at screening for GDM (weight change below, within, and in excess of the recommended range). They were respectively compared in each group.
Results Leptin, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and HOMA2-%B were increased in the group with pre-pregnancy BMI ≥25 kg/m2. Leptin and HOMA-IR were positively correlated with BMI both before pregnancy and at screening for GDM. There were no significant correlations between HOMA-IR and adipokines. HOMA-IR showed positive correlation with HOMA2-%B and negative correlation with HOMA2-%S.
Conclusion Leptin and HOMA-IR at diagnosed GDM were increased in the GDM patients with obesity before pregnancy. They were positively correlated with BMI both before pregnancy and at screening for GDM. The effect of maternal age at pregnancy and weight change during pregnancy at GDM screening on adipokines and insulin resistance might be less pronounced than the effect of maternal obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- L-ergothioneine reduces mitochondrial-driven NLRP3 activation in gestational diabetes mellitus
Colm J. McElwain, Andrea Musumeci, Samprikta Manna, Fergus P. McCarthy, Cathal M. McCarthy
Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2024; 161: 104171. CrossRef - The therapeutic effects of attending a one-day outpatient service on patients with gestational diabetes and different pre-pregnancy body mass indices
Yan-Min Cao, Min Ma, Wei Wang, Na-Na Cai
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Association With Anthropometric Fetal Indices
Tuan Dinh Le, Tien Minh Bui, Trinh Hien Vu, Nga Phi Thi Nguyen, Hoa Thanh Thi Tran, Son Tien Nguyen, Lan Ho Thi Nguyen, Manh Van Ngo, Hoang Huy Duong, Binh Thanh Vu, Hoa Trung Dinh, Binh Nhu Do, Duc-Cuong Le, Hien Thi Nguyen, Kien Trung Nguyen
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2022; 15: 117955142210984. CrossRef - New Insights into Adipokines in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Jorge Valencia-Ortega, Rebeca González-Reynoso, Edgar G. Ramos-Martínez, Aldo Ferreira-Hermosillo, María I. Peña-Cano, Enrique Morales-Ávila, Renata Saucedo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(11): 6279. CrossRef - The combination from ethanol extract of moringa leaves (Moringa oleifera L.) and ethanol extract of papaya leaves (Carica papaya L.) slows the tumor growth in sprague dawley rats induced 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene
Mutmainah Arif, Ika Yustisia, Padlianah
Medicina Clínica Práctica.2020; 3: 100100. CrossRef - Insulin resistance (IR) in pregnant women at the Mother and Child Hospital Khadijah, Makassar, Indonesia
Hasbobi Tabrang, Elizabet C. Jusuf, Himawan Sanusi
Enfermería Clínica.2020; 30: 84. CrossRef - Vitamin D Deficiency at Mid-Pregnancy Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Postpartum Glucose Intolerance in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 97. CrossRef - Involvement of the Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Bisphenol A (BPA) in Human Placentation
Sophie-Christine de Aguiar Greca, Ioannis Kyrou, Ryan Pink, Harpal Randeva, Dimitris Grammatopoulos, Elisabete Silva, Emmanouil Karteris
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 405. CrossRef - Joint Associations of Maternal Gestational Diabetes and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy With Overweight in Offspring
Yuying Gu, Jun Lu, Weiqin Li, Huikun Liu, Leishen Wang, Junhong Leng, Wei Li, Shuang Zhang, Shuting Wang, Jaakko Tuomilehto, Zhijie Yu, Xilin Yang, Andrea A. Baccarelli, Lifang Hou, Gang Hu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Reduced Serum Adiponectin Level and Risk of Poststroke Depression in Patients with Ischemic Stroke
Junhua Yang, Guanghui Du, Jinyu Wang, Jia Chen, Chenghui Yang, Jia Li, Yun Zhang
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2019; 28(2): 305. CrossRef - Letter: Adipokines and Insulin Resistance According to Characteristics of Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:457-65)
Ohk-Hyun Ryu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 87. CrossRef - The importance of treating mild hyperglycemia in pregnant women with diabetes
Kyung-Soo Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(6): 1079. CrossRef - Response: Adipokines and Insulin Resistance According to Characteristics of Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:457-65)
Eon Ju Jeon, Ji Hyun Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 90. CrossRef
- L-ergothioneine reduces mitochondrial-driven NLRP3 activation in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Others
- Cystatin C as a Predictor for Diabetes according to Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Korean Patients
- Eon Ju Jeon, Ji Hyun Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(1):32-34. Published online February 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.32
- 2,839 View
- 38 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic significance of serum cystatin C in acute brainstem infarctions patients
H. Li, B. Zhang, Z. Huang, H. Wu, B. Qin, L. Zhou, Z. Lu, F. Qin
Revue Neurologique.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - To compare the level of cystatin C in type 2 diabetes mellitus with obesity
Chahat Jhatta, Jashan Girdhar, Sumeet Gupta, Inderjeet Verma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 24(4): 312. CrossRef
- Prognostic significance of serum cystatin C in acute brainstem infarctions patients
- A Case of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.
- Myung Hwan Kim, Eui Dal Jung, Seung Pyo Hong, Gyu Hwan Bae, Sun Young Ahn, Eon Ju Jeon, Seong Yeon Hong, Ji Hyun Lee, Ho Sang Son
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(4):368-371. Published online July 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.4.368
- 2,047 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as glucose intolerance of variant severity with onset or first recognition during present pregnancy. Recently the prevalence of GDM in Korean has reported as 1.7~4.0%. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious metabolic complication of diabetes with high mortality if undetected. Its occurrence is very rare in gestational diabetes patients, but is harmful to fetal and maternal health. A 26 years-old pregnant woman was admitted at 37 weeks gestation because of progressive generalized weakness, anorexia and weight loss. Initial physical examination reveals that she had been dehydrated, and blood pressure 130/80 mmHg, pulse rate 100/min, respiratory rate 20/min, and body temperature was 36.9 degrees C. Serum glucose was 545 mg/dL, pH 7.282, HCO3- 10.5 mmol/L, urine ketone 3+, urine glucose 2+ when initial laboratory work was done. She was treated with intravenous fluid and insulin under the impression of diabetic ketoacidosis. Her delivery was performed after 24 hours from admission because of suggestive fetal distress. After recovery, she is being treated with insulin at outpatient department. We experienced a appropriately treated case of diabetic ketoacidosis in pregnant woman with GDM, and report it with a literature review.
- Microarray Analysis of Short Heterodimer Partner (SHP)-induced Changes in Gene Expression in INS-1 Cells.
- Eui Dal Jung, Ji Hyun Lee, Won Gu Jang, Jung Guk Kim, Bo Wan Kim, In Kyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(3):193-199. Published online May 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.3.193
- 1,817 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Nuclear receptors are involved in the cell growth, development, differentiation, and metabolism. The orphan nuclear receptor SHP which lacks a DNA-binding domain is a negative regulator of nuclear receptor signaling pathways. In pancreas, SHP regulate transcriptional activity of HNF3 and HNF4 through binding them and BETA2 which is involved in beta cell differentiation and insulin production. Here, we examined transcriptional activity changes of genes expressed in beta cell when SHP was overexpressed. METHOD: INS-1 cells of passage number 24 - 30 were prepared. Affimetrix DNA chip was used to examine gene expression in INS-1 cell when SHP was overexpressed. INS-1 cells were infected with adenovirus-SHP to overexpress SHP. To confirm the result of DNA chip, we used real time RT-PCR. RESULT: When SHP was overexpressed by adenovirus-SHP transfection, FXR, Transforming growth factor, beta 2, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 2, bone morphogenetic protein 4 genes expression were increased. Contrarily, Activating transcription factor 2, Glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha, Nur 77, fibroblast growth factor 14 genes expression were decreased. We confirmed DNA microarray analysis by real time RT-PCR. FXR, tribbles homolog 3 (Drosophila), fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 2, CD36 genes expression were increased in real time RT-PCR. Nur 77 and cAMP response element modulator genes expression were decreased in real time RT-PCR. CONCLUSION: we identified several genes which expression are regulated by SHP in pancreas beta cell. These results help to explain how SHP act in the various metabolism of pancreas beta cell.
- The Thickness of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness in Hypertriglyceridemic Hyperapo B Type 2 Diabetes.
- Ji Hyun Lee, Duck Soo Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(1):57-64. Published online January 1, 2005
- 781 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Atherosclerotic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease are major causes of diabetes mellitus-related morbidity and mortality. The frequency of macrovascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients varies geographically, and this suggests that factors other than diabetes play an important role in the pathogenesis of their vascular disease. One such factor may be the dyslipoproteinemias that are common in diabetic patients. There were many studies showing that hypertriglyceridemia with an elevated apolipoprotein B (apo B) level was associated with an increased risk for coronary disease in type 2 diabetes patients. Meanwhile, an increase in the intima-media thickness (IMT) of the carotid artery has been previously reported in patients with type 2 diabetes, and this is related to the atherosclerotic risk factors. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the carotid artery IMT and lipoprotein and apolipoprotein, and we also wanted to assess the role of hypertriglyceridemic hyperapo B for the cardiovascular risk factors in the type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: The carotid artery IMT was measured using high resolution B-mode ultrasono graphy in 117 type 2 diabetes. At the same time, we analyzed the patients characteristics including height, weight, body mass index, blood pressure, duration of diabetes and history of hypertension. Laboratory parameters such as fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, apolipoprotein A and B were included in this study. We defined hypertrigl yceridemic hyperapo B as when the triglyceride level was over 1.7 mmol/L and the apolipoprotein B level was over 1.20 g/L. RESULTS: Thirty-three patients (28%) were classified as having hypertriglyceridemic hyperapo B. Age (r = 348, P = 0.001), duration of diabetes (r = 0.438, P = 0.001), hypertension (P = 0.001), and LDL-cholesterol (r = 0.225, P = 0.018) were statistically significant for the carotid artery IMT values in diabetic patients. However, there were no correlations between carotid artery IMT and total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL- cholesterol, and apolipoprotein A and B. Upon multiple regression analysis, age, duration of diabetes and LDL-cholesterol were statistically significant for the carotid artery IMT values in diabetic patients (R2 = 0.296). Hypertriglyceridemic hyperapo B diabetic patients didn't have higher carotid artery IMT values than the other patients. CONCLUSION: The increment of carotid artery IMT is affected by age, blood pressure, duration of diabetes and LDL-cholesterol. However, our study did not show any association between carotid artery IMT and hypertriglyceridemic hyperapo B
- The Correlation Between Femoral Artery Intima-Media Thickness (IMT) and Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.
- Ji Hyun Lee, Ho Sang Shon, Duck Soo Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(6):467-475. Published online December 1, 2003
- 1,001 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
High resolution B-Mode ultrasound is increasingly used in epidemiological and clinical research to noninvasively study the atherosclerotic process in the carotid artery. An increase in the intimamedia thickness (IMT) of the carotid artery has previously been reported in patients with diabetes, compared with a control group, and is related to atherosclerotic risk factors. There have been few reports on the relationship between the IMT of the femoral artery, another large artery, and atherosclerotic risk factors in diabetic patients. The aim of the present investigation was to evaluate the relationship between the femoral artery IMT and the atherosclerotic risk factors in type 2 diabetics, and to assess if such a measurement might provide further information on the extent of the atherosclerotic disease in these patients. METHODS: The carotid and femoral IMT were measured using high resolution B-mode ultrasonography in 55 type 2 diabetes patients and 25 age- and sex-matched control subjects. The femoral artery was examined distal to the inguinal ligament, at the site the artery divides into the superficial femoral and the profound femoral arteries. At the same time, patient's characteristics, including height, weight, body mass index, blood pressure, duration of diabetes and histories of hypertension and smoking, were analyzed. Examinations of the laboratory parameters, such as serum glucose, HbA1C, lipid profile, blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, were included in this study. RESULTS: The carotid and femoral IMT values were significantly increased in the type 2 diabetes patients compared with the control subjects. There was a significant relationship between the IMT values of the two arteries in the diabetic patients (r=0.419, p< 0.001). In a simple regression analysis, age (r=0.534, p=0.001), systolic blood pressure (r=0.499, p=0.001), diastolic blood pressure (r=0.350, p=0.003), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (r=-0.262, p=0.037) and the serum creatinine level (r=0.280, p=0.020) were statistically significant for the femoral artery IMT value. In a multiple regression analysis, age, smoking and systolic blood pressure were statistically significant for the femoral artery IMT values in diabetic patients (R2=0.379). CONCLUSION: The femoral IMT values were significantly increased in the type 2 diabetes patients. Increases in the IMT of the femoral artery are affected by the atherosclerotic risk factors; age, smoking and blood pressure. Therefore, it is suggest that measurement of the femoral IMT, using high resolution B-mode ultrasonography, is also a useful method for the detection of macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes patients.
- A Case of Interstitial Deletion [del(6)(q21q23)] with type 2 diabetes Mellitus and Mental Retardation.
- Ye Dal Jung, Sun Joo Cho, Hak Jun Kim, Wern Chan Yoon, Dong Geun Yeo, Jeong Ki Park, Ji Hyun Lee, Ho Sang Shon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2000;24(2):281-284. Published online January 1, 2001
- 973 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Chromosomal abnormalities such as Klinefelter syndrome, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Prader-Willi, Bardet-Biedl syndrome were associated with diabetes mellitus. Over 30 cases of interstitial deletions of the long arm of chromosome 6 with vastly variable breakpoints and clinical features have been reported in the literature, The clinical findings varies and most often includes mental retardation, microcephaly, and craniofacial anomalies. We report a case of interstitial deletion (del(6)(q21q23)) with type 2 diabetes mellitus and mental retardation.
- The Difference of Intrarenal Hemodynamics in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy.
- Ji Hyun Lee, Ye Dal Jung, Ho Sang Shon, Ki Sung Ahn, Duck Soo Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 1999;23(6):822-830. Published online January 1, 2001
- 946 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Diabetic nephropathy is a major microvascular complication in diabetic patients. No single etiologic factor has been identified to explain the development of diabetic nephropathy. Genetic factors, poor glycemic control, increased intra-glomerular pressure, systemic hypertension, and altered intrarenal hemodynamics may be contributed to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Intrarenal duplex Doppler sonography can provide physiologic information reflecting the status of renal vascular resistance. Recently, there were some reports that obstructive renal disease and renal allograft rejection patients has altered intrarenal hemodynamics. So we investigate intrarenal hemo- dynamic abnormalities in diabetic patients with nephropathy and analyze the factors associated with increased intrarenal resistance METHODS: The patients were divided into the three groups. According to the levels of 24-hour urinary albumin excretion(UAE), group 1 (UAE<30mg/day, normoalbuminuria), group 2 (30 mg/day
- Angiotensin 1 Converting Enzyme ( ACE ) Gene Polymorphism According to Micro- and Mocro - angiopathy in non-insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus.
- Moon Suk Nam, Hyun Chul Lee, Ji Hyun Lee, Bong Soo Cha, Su Youn Nam, Young Duk Song, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Kap Bum Huh
- Korean Diabetes J. 1997;21(4):397-405. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,019 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Chronic micro- and macro-angiopathy in diabetes are clinically significant complications that affect both quality and length of life in diabetic patients. Angiotensin 1 converting enzyme (ACE) is of key importance in regulating systemic and renal circulation by converting angiotensin-1 into -2 and inactivating bradykinin, Recent reports suggest that the ACE gene polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to micro- and macro-angiopathy in diabetes. But the results are diffetent according to the type of diabetes and complication. METHODS: We investigated the alleles of the ACE gene and measured the ACE activity in the 169 cases of non-insulin dependent diabetic patients and in the 95 cases of controls matched with age and BMI. RESULTS: The measured ACE activity was well correlated with the count of D allele. We found no differences of ACE alleles between in diabetes and control. No association was found between ACE gene polymorphism and diabetic microangiopathy(retinopathy or nephropathy). But DD genotypes (homozy-gotes for the deletion polymorphism) and D allele were found more frequently in diabetic patients with coronary artery obstructive diseases than in patients without coronary artery obstructive diseases in coronary angiography. CONCLUSION: These data indicate that ACE gene polymorphism in non-insulin dependent diabetes is associated with coronary artery obstructive diseases, but not with chronic microangiopathy.
- Relationship between Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphism and Vascular complications in Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetic Patients.
- Byoung Gue Na, Tae Geun Oh, Sang Moo Jung, Sang Woo Oh, Jae Hong Choi, Ji Hyun Lee, Seong Su Koong, Seung Taik Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 1997;21(2):138-146. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,070 View
- 16 Download
- Thebeta3-adrenergic Receptor Gene Polymorphism in Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus.
- Ji Hyun Lee, Hai Ri Li, Sang Won Lee, Su Youn Nam, Young Jun Won, Bong Soo Cha, Moon Suk Nam, Young Duk Song, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
- Korean Diabetes J. 1997;21(2):130-137. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,229 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The B3-adrenergic receptor, located mainly in adipose tissue, is known to be involved in the regulation of lipolysis and thermogenesis. Recently studies have shown that the B3-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism is associated with Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus(NIDDM) and insulin resistance. We investigated the relationship between the B3-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism and the cli!ical and biochemical features of NIDDM patients. METHODS: Anthropometeric and biochemi al characteristics were determined for 134 NIDDM subjects and 30 nondiabetic controls. All subjects were genotyped for the 0-adrenergic receptor gene mutation using restriction fragment length polymorphism assay. RESULTS: The allelic frequency of the mutated allele was similar in NIDDM subjects and nondiabetic controls(11%, 12% respectively). There was no difference in the Arg64 allelic frequency of the B3-adrenergic receptor gene according to the onset age of diabetes. In diabetic group, the clinical and biochemical characteristics were not statistically different between the B3-adrenergic receptor gene mutation and nonmutation group. In control group, also no clinical differences were found between mutation and non-mutation group. When comparing frequency of obesity according to the B3-adrenergic receptor gene mutation in diabetic patients, we did not find the difference between the two groups. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that the b3-adrenergic receptor gene is not a major determinant for the development of obesity and NIDDM in Korea.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





